Outline:
With the widespread growth of cloud accessibility, traditional software development may appear more arduous in comparison to solutions offered by computing power and centralized hosting services. Among the many options available, Software as a Service (SaaS) development provides a convenient means for engineers to deploy applications more efficiently, rapidly, and at a lower cost. This flexibility allows for the availability of almost every type of core business function via the web. If you are interested in obtaining a better understanding of SaaS or exploring key characteristics of Saas and its benefits, this is the ideal place to get answers to your questions.
The Evolution of SaaS Model: From Mainframe Computers to Cloud Computing
The concept of centralized hosting for applications dates back to the 1960s, when mainframe computer providers like IBM began offering utility computing services to large organizations and banks. These services offered computing power and database storage to clients.
With the rise of the internet during the 1990s, a new class of centralized computing emerged, providing specialized business app hosting and management to small businesses. Application Service Providers (ASPs) greatly reduced costs through central administration, making their services more valuable.
This new wave of centralized computing laid the foundation for the growth of cloud computing, which initiated the development of companies dedicated to creating cloud software. Salesforce, one of the earliest players in the SaaS market, began offering traditional enterprise solutions, such as customer relationship management (CRM), through an early SaaS model.
Today, SaaS has revolutionized the way businesses operate, providing them with easy access to a range of software applications, and helping them to save costs and increase efficiency.
Understanding Software as a Service: Features and Key Characteristics of SaaS Applications
In a nutshell, Software as a Service is a licensing and delivery model that allows software to be accessed via the internet on a subscription basis. It is also known as web-based or web-hosted software. The working principle of SaaS applications is that they run on a SaaS provider’s servers. The provider hosts the application and any related data on its own servers, databases, and networking resources, or employs an Independent Service Vendor (ISV) that contracts with a cloud provider to host the application in a particular data center.
With SaaS, there is no need to download the software to your PC or business network to manage it. Instead, the provider administers access to the application through a web browser, including monitoring its availability, performance, and security. Users simply pay a subscription fee to gain access to the application, which eliminates the need for a complicated installation process or maintenance. This makes SaaS a popular option for most businesses, along with other numerous benefits provided by a SaaS solution.
The Competitive Advantage of SaaS Architecture
The architecture of Software as a Service is one of its primary competitive advantages. SaaS typically adheres to a multitenant approach, where all users and applications share a common infrastructure with a single version and configuration across all customers, and one code base that is centrally maintained.
This approach allows for faster updates and bug fixes, as well as easier deployment of changes, since engineers can innovate for all customers by administering the one shared instance, rather than handling several instances at once. It guarantees a bigger pool of resources to be available to a larger public without compromising any essential cloud functions like security, speed, or privacy.
In a multitenant architecture, all users share the same infrastructure and resources, yet their data is kept separate and safe. This ensures that all customers can benefit from the same level of performance and security, while also reducing costs and increasing efficiency. This architecture also allows for scalability, as it can accommodate more users and applications with ease.
The Key Benefits of Using Software as a Service Model
Software as a Service offers several benefits over traditional software delivery models. Here are some of the most significant advantages of using SaaS:
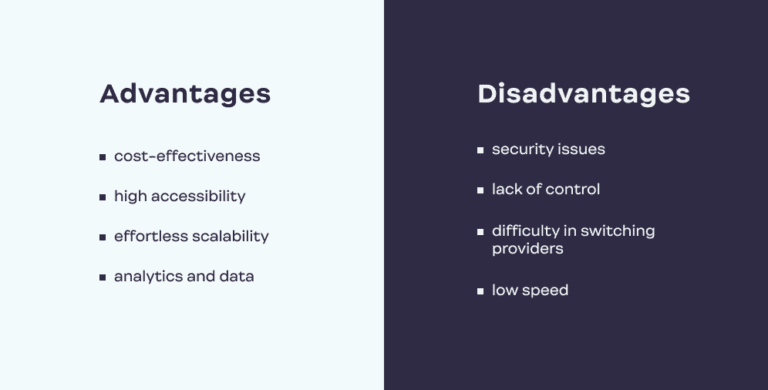
Cost-Effectiveness: Eliminating the Need for Hardware Acquisition
One of the most crucial benefits of SaaS is its cost-effectiveness. With SaaS, businesses can eliminate the need for hardware acquisition, installation, and support, which can be one of the most prominent SaaS benefits for businesses on a budget. The model operates on a subscription basis, allowing business owners to predict their finances more precisely and save costs.
High Accessibility: Running on Any Operating System and Mobile Devices
SaaS applications can run on any operating system via an internet browser, making them accessible to all users. Additionally, applications can be used on mobile devices like tablets, ensuring accessibility in different circumstances and locations.
Effortless Scalability: Adding or Reducing Users With Ease
SaaS makes it easy to add or reduce users by simply adjusting your billing plan accordingly, making it a highly scalable model.
Cloud-Based Data Storage and Easy Device Switching
With SaaS, data is saved in the cloud, eliminating the need for backups and other disaster recovery plans to handle any hardware collapses. Users can switch between devices without risking losing previous work and data progress simply by logging into a single account regardless of the device.
Centralized Platform for Capturing Data and Conducting Analytics
SaaS applications run through a centralized platform, making it easier to capture data and conduct analytics. Vendors who use SaaS can access reporting and intelligence tools, helping them streamline their workflow and get valuable insights.
UI Customization and Feature Switching for Personalized Experience
SaaS offers customization, especially across applications from one software provider, allowing businesses to adjust the look and feel of the program according to their needs. Additionally, web-based software allows businesses to switch off and on several business features to make their products even more personalized.
In conclusion, the SaaS model provides businesses with several advantages, including cost-effectiveness, high accessibility, effortless scalability, reliable saving and storage, powerful analytics and data, and customization. These benefits make SaaS a highly attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
SaaS Risks and Challenges: Revealing the Dark Side of Software as a Service
Despite all SaaS advantages to businesses, there are also risks and challenges associated with this model. Here are some of the vital points to consider:
Security Issues: Relying on External Vendors for Software Safety
One of the major concerns with SaaS is security. Since data is stored on external servers, businesses must rely on outside vendors to provide software safety. This means they have to ensure that data is secure and cannot be accessed by unauthorized parties. The security risks associated with SaaS can be a real obstacle, including concerns such as encryption, security monitoring, and costs of external tools to offset SaaS security challenges.
Lack of Control: Limited Ability to Control Updates and Versioning
SaaS providers roll out updates and changes to all customers regardless of their preferences and needs. Customers may require extra time for training, especially when the changes are important. It also means customers cannot control versioning, making it challenging to adopt a renewed version quickly.
Difficulty in Switching Providers
Migrating to another vendor can be difficult, as customers must migrate large amounts of data. If the vendor uses proprietary technologies, it can make migrations between different cloud providers even more challenging.
Low Speed: Performance Issues Due to Slow Internet Connections
Slow internet connections can be a problem for SaaS, especially when the cloud servers are accessed from far distances. The remote nature of SaaS features can sometimes lead to performance issues.
In conclusion, while SaaS offers several benefits, it also poses significant risks and challenges, including security concerns, limited control over updates and versioning, difficulty in switching providers, and low speed. Understanding these risks and challenges is essential for businesses to make informed decisions when choosing SaaS solutions.
Top SaaS Providers for Businesses & Examples
Despite all these SaaS challenges, the SaaS market involves a variety of software providers and products and only continues to grow. The scope ranges from small industry players and single-product vendors to real industry giants. One of them is Google, with its online word processor, Google Docs. To work with it, users need to log in on any web browser for instant access. This SaaS product allows writing, editing, and even collaboration in real-time wherever users’ locations are.
Another great case is Dropbox. It is cloud storage where businesses can store, share, and collaborate on different types of files and data, including visuals, photos, and videos.
Those not acquainted with the SaaS concept might be surprised, but Netflix is also a SaaS company that sells software to watch licensed videos on demand. It uses a subscription model, allowing users to choose a pricing plan with a fixed sum of money paid monthly or annually.
All in all, the SaaS market is everything in one place, and here you can find applications for fundamental business processes like management, human resource management, billing, and collaboration. If you seek enterprise solutions, you can use vertical SaaS products that are specifically created for one particular industry or narrow market niche, such as commerce or insurance. Horizontal SaaS models target a broad cycle of customers, not regarding their core industries. The most prominent examples of this type of SaaS are SalesForce and HubSpot.
SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS: Understanding the Differences
To understand the essence of Software as a Service (SaaS), it’s critical to explore it in the context of other cloud service models. Here is a comparison of the three main as-a-service products: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS:
SaaS
SaaS is a fully managed product that delivers applications by subscription. SaaS vendors handle maintenance, updates, support, and other aspects of administering the software. Users don’t have to worry about hardware acquisition, installation, or maintenance, as all these tasks are handled by the provider.
PaaS
Platform-as-a-service (PaaS) provides a software development platform or a framework of resources for developers. This web-hosted platform allows engineers to develop customized applications and concentrate on software creation without focusing on storage or infrastructure issues. PaaS vendors are responsible for providing related tools and managing the infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking hardware.
IaaS
Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) is a more fit solution for companies that want to outsource their data center and other resources to a cloud provider. This type of product usually hosts infrastructure elements, including servers, networking hardware, or storage that are available for purchase. IaaS services require self-maintenance, meaning IaaS users have to manage their data use and applications themselves.
When comparing SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS, SaaS is a complete and fully managed product that delivers applications by subscription, whereas PaaS provides a development platform for engineers to create customized applications without worrying about infrastructure issues. Finally, IaaS is a suitable option for companies that want to outsource their data center and other resources to a cloud provider.
In conclusion, each as-a-service product offers unique features and functionalities, making them suitable for various types of businesses. Understanding the differences between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS is essential when deciding which cloud service model to adopt for your business.

SaaS Pricing Models: Choosing the Right One for Your Business
One of the most significant advantages of SaaS is cost-effectiveness. However, pricing plans can be quite versatile, making it crucial for businesses to choose the right pricing model to organize their budget effectively. Here are some of the most common SaaS pricing models:
- Free or Ad-based: This model offers free usage of the service, but SaaS providers generate profit through selling space for advertisements. It usually presupposes an upgrade to a paid version that won’t show advertisements.
- Flat-rate Pricing: With this model, users pay a fixed subscription fee monthly or annually to get access to the service.
- Per-User Pricing: Pricing is determined by the number of users accessing the service, and there can be a fixed fee for every customer.
- Storage Fees: Although users may access the service for free, they still need to pay for storage if they want to continue working with the SaaS product after the gratuitous limit is over.
- Feature-based Pricing: In this model, fees are determined by the number of features the user employs. Thus, incomplete versions with limited features would cost less than the maximum supply of functionalities.
- Freemium Pricing: With this model, the service provider offers basic entry-level features for free while charging a premium for any additional advanced functionalities. However, users may face restrictions in order to upsell a paid version.
On a Final Note
Overall, the benefits of the software as a service model are substantial for both vendors and users. Although some may prefer traditional cloud management services and software, SaaS provides tremendous opportunities for most small businesses to develop and expand with fewer efforts and costs, providing them with ready-made solutions.
Moreover, organizations are now seeking ways to develop SaaS integration platforms to manage the process of connecting SaaS features and solutions to other cloud-based applications or systems into larger units. This indicates that software-as-a-service will continue to grow, offering an even better experience for those who work with it.
If you still have questions about SaaS or want more insights about software as a service risks, please feel free to contact us. We will provide you with all the necessary information to satisfy your interest.